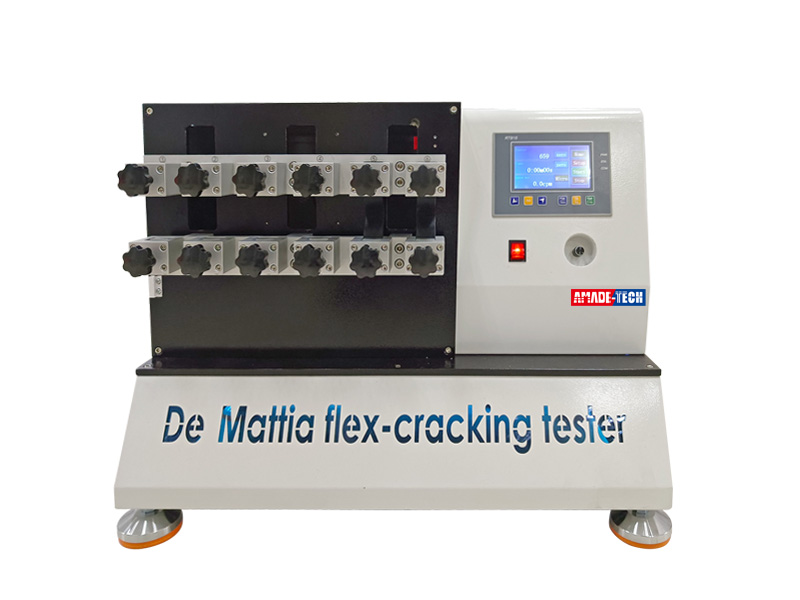
DeMattia Flexing Fatigue Tester China Manufacturer
DeMattia Flex Tester is also called the DeMattia flexing fatigue tester. It is used to determine the resistance of vulcanized or thermoplastic rubbers to the formation and growth of cracks when subjected to repeated flexing or extension.
When measuring the ability to resist flexing-fatigue cracking, a circular molded groove of the specified size is required at the midpoint of the longitudinal length of the specimen and is perpendicular to its longitudinal axis. To determine the crack growth, the bottom of the groove at a point equidistant from the sides needs to be pierced by a piercing spear, which artificially initiates cut growth in the flex area of the specimen to make it prone to cracking.
Besides rubber specimens, It is also applicable to coated leathers, soles, and coated fabrics.
AmadeTech DeMattia flex tester is available in 1 row or 2 rows of gripping devices to hold 6 pcs or 12 pcs of the specimens at a time. For 12-station machine, it shares the same movable assembly in the middle. Specimens in one row are flexed, while the specimens in the other row are straightened during the test.
The selection of the grip number depends on your requirements. Please advise us of your preference when sending the inquiry.
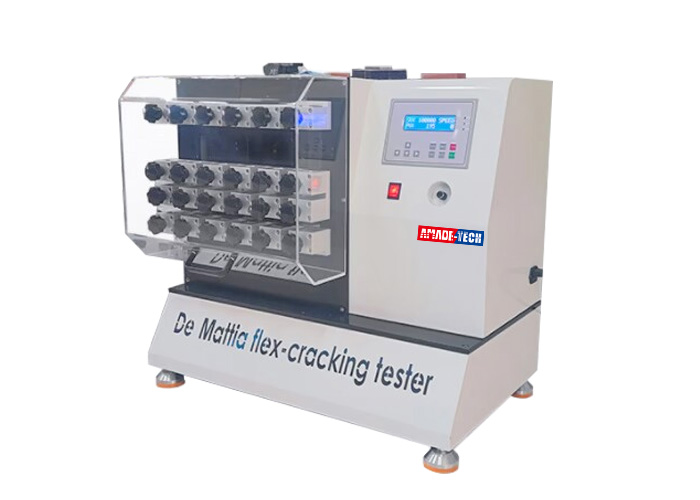

12-station DeMattia machine
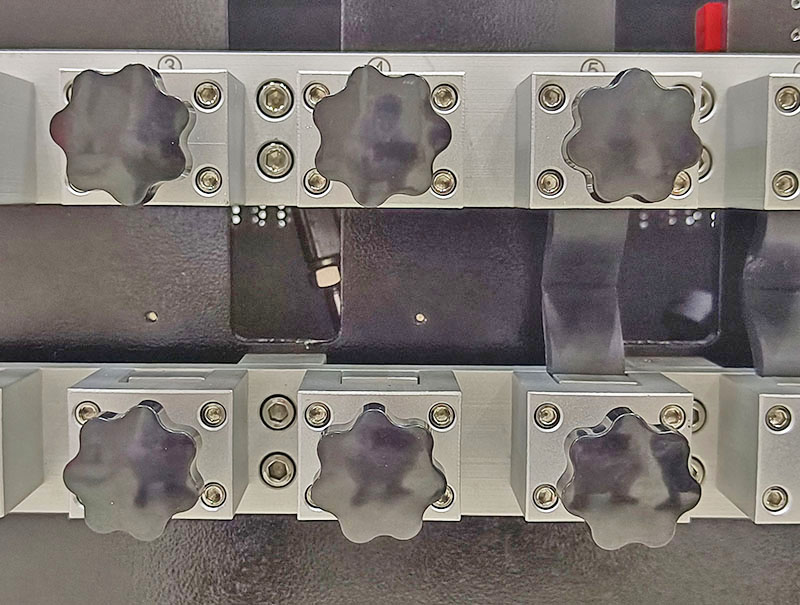
Sampe holding devices
A stationary grip and a movable grip are arranged at the same vertical plane and with both vertical axes on the same vertical line to form a pair of opposing gripping devices. Each grip consists of a jaws under control by the screw. As loosing the screw, the gap between the jaws widens, allowing you to insert the specimen lengthwise from above. For the determination of crack growth, an artificial cut is required to be made in the sample by a piercing tool to initiate cut growth. Two ends of the specimen are held by the stationary and movable grips, respectively. The movable grip is able to reciprocate vertically in a straight line with a travel of 57 mm to generate a maximum separation of 76 mm and a minimum separation of 19 mm. A constant-speed motor drives the movable grip by means of the eccentric and connecting rod, enabling fast movement as high as 300 cpm.
You are available to set a desired number of cycles before the commencement. The real-time number of cycles is displayed on the screen while the test is running. The machine stops automatically once the predetermined number of test cycles is achieved.
If required, AmadeTech can supply a DeMattia flexing machine with a chamber to give the specimen under test specified low or high temperature and humidity conditions.
Test Standards
ASTM-D813 ASTM-D430, BS-903, ISO-132, GB/T13934, GB/T13935, JIS-K6301 etc.
DeMattia Flexing Fatigue Test Principle
A pair of opposing grips is separated to the maximum distance. One end of the test piece is mounted in the stationary clamp, and the other end is secured in the movable clamp, ensuring that the groove is parallel to the bending axis and sits symmetrically midway between the upper and lower clamps. Visual examinations at frequent intervals are needed after machine actuation until the first small sign of cracking is detected on the specimen to determine the flex cracking, or measurements of cut length at frequent intervals are required to determine the crack growth.
Core Technical Parameters
| Model | AT-R7016 |
| Test Station | 6, 12 or specified |
| Specimen size | (140 ~ 155) x (20 ~ 25) x 6.3 mm |
| Grip spacing | 19 ~ 75 mm |
| Reciprocation travel | 57 mm |
| Test speed | (300±10) CPM adjustable |
| Counter | 0 ~ 999,999 |
| Dimension | 55 x 44 x 69cm |
| Weight | 78 kg |
| Power | 1 phase, AC220V / 110 V±10%, 3A |
DeMattia Flex Tester Features
- Capable of conducting flex cracking tests and crack growths.
- As many as 12 test pieces can be clamped into one machine and tested at the same time.
- Powered by an excellent motor with constant velocity to drive the flexing run.
- The flexing cycles can be counted automatically and presented via the digital screen.
- Easy accessibility with simple buttons and operation.
- Complies with different international and domestic test standards.
FAQs
Request a Quote Now
Please feel free to contact us for more details on the product, price, lead time, payment terms, shipment methods, etc. Amadetech sales specialists will respond within one working day.




