The temperature and humidity test chamber is also called a humidity chamber, a programmable heat and humidity alternating test chamber, a climate chamber, or an environmental chamber. It can imitate the high temperature, low temperature, and humid and dry climate conditions in the natural environment to verify the heat, cold, dry, and humidity resistance of materials or products under specific temperature and humidity conditions.
It can also be used to store routine samples in the laboratory or to perform necessary temperature and humidity conditioning on samples before testing. A temperature and humidity test chamber is essential equipment for a standardized laboratory.
Inner Chamber Volumes | 80 L, 150 L, 225 L, 408 L, 800 L, 1000 L, etc. (optional) |
Core Materials | 304 stainless steel & cold rolled steel |
Reachable Temp. Range | 0~150℃,-20~150℃,-40~150℃,-70~150℃,etc. (optional) |
Temperature Resolution | 0.01℃ |
Temperature Fluctuation | ±0.5℃ |
Temperature Uniformity | ±2℃ |
Temperature Accuracy | ±0.1℃ |
Cooling Rate | Average 1℃/min, nonlinear without load |
Heating Rate | Average 3℃/min, nonlinear without load |
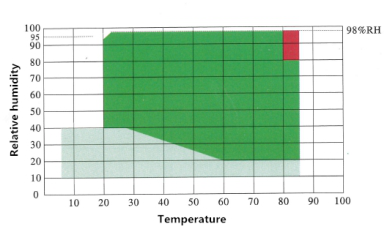
Humidity Range | 20% R.H ~ 98% R.H |
Humidity Fluctuation | ±2.5% R.H. |
Humidity Uniformity | +2, -3% R.H. |
Temperature/Humidity Control Chart |
How to Choose a Suitable Temperature and Humidity Test Chamber?
The maximum and minimum temperature your samples require and the humidity range you need to control
According to different models, the lowest temperature that our conventional humidity chambers can achieve are 0 degrees, -20 degrees, -40 degrees, and -60 (-70) degrees, and the controllable humidity range is usually 20% ~ 98%RH unless special requirements for humidity as low as 10% R.H. or even 5% R.H.
How much test space do you need to accommodate the specimens
Our regular inner box capacity includes 80L, 100L, 150L, 225L, 408L, 800L, and 1000L. In addition, multiple movable shelves can be arranged in the chamber for placing your samples based on your requirements.
The site conditions where you install and use this temperature and humidity test chamber
Suppose your lab is located in an office building. In that case, you should consider a small temperature and humidity control chamber because most office areas have narrow elevators or doors to allow your equipment to enter. Moreover, you have to consider that the power supply in the office area is mostly single-phase 220V or 110V.
If your test venue is large enough, you can choose a large-sized humidity chamber, an automatic water supply device, and a tap water filter. Our sales consultants will recommend specific constant temperature and humidity chamber models according to your requirements.
Main Structures of the Humidity Chamber from AMADE TECH
The structures of the humidity test chamber comprise a box body, refrigeration system, heating system, humidification and dehumidification system, temperature and humidity controller, air supply circulation system, temperature and humidity measurement devices, etc.
Box Body
The inner and outer boxes of the temperature and humidity test box are formed by sheet metal processing. The plates in the test area are welded with SUS304 stainless steel. The box shell is welded with A3 steel plates, and anti-static spraying is used to prevent rust on the surface. You can also select SUS304 stainless steel without painting as the shell material. The environment-friendly polyurethane foam thermal insulation material is filled between the inner box wall and the outer box, and the temperature isolation effect is very good.
The door is equipped with anti-aging silicone sealing strips, effectively isolating the heat exchange inside and outside the chamber. It is not recommended to open the chamber door to observe the sample during the test, so we installed a multi-layer tempered glass window on the door and installed an independent light on the window to facilitate your observation. Some product samples may need to be connected to external power or cables when testing, so our standard humidity chamber is equipped with a 50 mm or 100 mm diameter wire hole on the left side.
Refrigeration System
The refrigeration system is one of the key parts of the constant temperature and humidity test chamber. The refrigeration methods we use are fully mechanical refrigeration, which is vapor compression refrigeration. They are mainly composed of a compressor, condenser, throttling mechanism, and evaporator. The refrigeration system of the constant temperature and humidity test chamber consists of two parts: the high temperature and the low temperature. Each part is a relatively independent refrigeration system. The evaporation of the refrigerant in the high-temperature part absorbs the heat of the refrigerant from the low-temperature part to vaporize. The evaporation of the refrigerant in the low-temperature part absorbs heat from the object to be cooled to obtain the cooling capacity. The high-temperature and low-temperature parts are connected by an evaporative condenser, which is both the condenser of the high-temperature part and the condenser of the low-temperature part.
If the required low temperature of your test is -50 ℃, it is difficult to meet the requirements using single-stage refrigeration. Therefore, the refrigeration method of the temperature and humidity test chamber generally adopts cascade refrigeration. The medium and low-temperature refrigerant we use is Honeywell R404A or the alternative R449A. The ultra-low temperature refrigerant we use is R23.
Heating System
The heating system and the principle of temperature control are much simpler than the refrigeration system. It generates heat by means of electric heating of nickel-chromium alloy wire and adopts a non-contact control method. The heating device is the key component for heating up the constant temperature and humidity testing machine. After the controller gets the heating command, it outputs the voltage to the relay. About 3 ~ 12 volts DC is applied to the solid-state relay. Its AC end is equivalent to the wire being connected, and the contactor is also pulled in at the same time. The voltage at both ends of the heater causes it to heat up.
The circulating fan transfers the heat into the chamber to heat up the test space. When the temperature is about to reach the set value, the controller adjusts on and off through the solid state relay. The constant temperature and humidity test chamber is controlled by the solid state relay to control the heating of the heater and the cooling of the compressor to achieve a dynamic balance of temperature.
Temperature & Humidity Control System
The control system is one of the core components of the constant temperature and humidity test chamber. It determines important indicators such as the heating and cooling rate of the testing machine and the accuracy of temperature and humidity. It can realize programmable multi-stage temperature and humidity cycle control, fault detection and equipment safety protection, etc.
Humidification & Dehumidification System
The humidification method generally adopts the steam humidification method. That is, the low-pressure steam is directly injected into the test space. The humidification speed is fast, the humidification control is sensitive, and it is easy to achieve forced humidification, especially when the temperature is lowered.
There are two dehumidification methods: mechanical refrigeration dehumidification and dry dehumidification. The dehumidification principle of mechanical refrigeration is to cool the air below the dew point temperature so that the water vapor greater than the saturated moisture content is condensed and precipitated, thus reducing the humidity. The dehumidification of the dryer is to use the air pump to extract the air in the test space, then inject the dry air into the test space. At the same time, the moist air is sent to a recyclable dryer for drying and then sent to the test space after drying. Repeat this cycle for dehumidification. Most of the comprehensive test chambers now use the first dehumidification method and the second dehumidification method, which can make the dew point temperature below 0 °C, but the cost is more expensive.
Air Supply Circulation System
The air circulation system is generally composed of a centrifugal fan and a motor that drives its operation. It provides air circulation in the constant temperature and humidity test chamber so that the temperature in the chamber is uniform and stable.
Sensors
The sensors are a temperature sensor and a humidity sensor, which are located in the test space. The temperature sensor is a platinum resistor. The measurement method of humidity is using wet bulb gauze.
Safety Measures
Our constant temperature and humidity test chambers are equipped with multiple protection measures. The temperature system is equipped with an over-temperature protector. The air heating element can be automatically cut off when the rotating fan is stopped. The humidification system can automatically stop the power supply when the water level of the humidification tank decreases. The refrigeration system can also automatically stop working when the temperature of the box rises (over 40°C) or the humidity increases.
Maintenance of the Temperature Humidity Chamber
Regular maintenance of the constant temperature and humidity chamber helps maintain good performance and prolong the life of the machine.
First, the constant temperature and humidity chamber must be installed in a ventilated, dry and clean place, and the working environment temperature should be kept at (20 ± 5) ℃.
1. Cleaning of the test area: After each test, the debris in the chamber should be wiped clean with a cloth or cleaned with a vacuum cleaner. Clean the chamber’s interior surfaces with a damp cloth and mild detergent or stainless steel cleaner. Anti-rust oil can be applied regularly.
2. The shell of the temperature and humidity test chamber should be cleaned regularly with a damp cloth and mild detergent. The cleaning agent used should ensure that it does not damage the paint surface. If it is a stainless steel shell, it needs to be sprayed with anti-rust oil.
3. Regularly check the air-cooled condenser. You can use compressed air or a vacuum cleaner with a brush to clean the dust on the condenser. It can prevent high energy consumption caused by poor heat dissipation and the high-pressure alarm of the compressor.
4 The refrigeration system is the heart of the machine. Please check all copper pipes once a year for leakage of refrigerant and leakage of welding joints. If oil leaks, the repair is required.
5 The inside of the distribution box should be cleaned and inspected regularly. Loose contacts can put the entire device in a dangerous working state, possibly resulting in component burnout. When cleaning, you can use a vacuum cleaner to remove dust from the distribution box.
6. Drain the water in the humidifier regularly, and clean the scale with a towel or rag. It prevents damage to the humidifier.
7. The water tank needs to be cleaned regularly to prevent the pipeline from clogging.
Request a Free Quote Now